- Se Atomic Number Formula
- Se Atomic Mass
- Se Atomic Number Definition
- Se Element Charge
- Se Atomic Number Meaning
- Se Atomic Number Symbol
- Se Atomic Number Periodic Table

Se Atomic Number Formula
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope. (Atomic mass is also referred to as atomic weight, but the term 'mass' is more accurate.)
For instance, it can be determined experimentally that neon consists of three isotopes: neon-20 (with 10 protons and 10 neutrons in its nucleus) with a mass of 19.992 amu and an abundance of 90.48%, neon-21 (with 10 protons and 11 neutrons) with a mass of 20.994 amu and an abundance of 0.27%, and neon-22 (with 10 protons and 12 neutrons) with a mass of 21.991 amu and an abundance of 9.25%. The average atomic mass of neon is thus:
| 0.9048 | × | 19.992 amu | = | 18.09 amu |
| 0.0027 | × | 20.994 amu | = | 0.057 amu |
| 0.0925 | × | 21.991 amu | = | 2.03 amu |
| 20.18 amu |
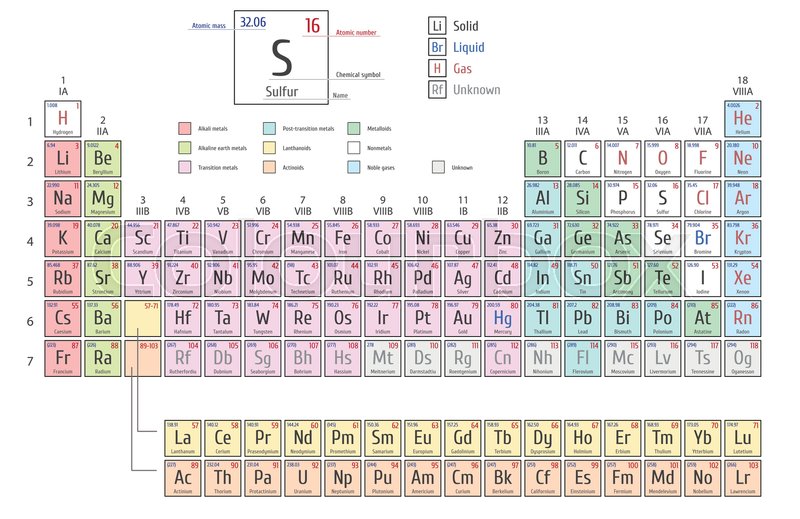
1: Selenium An element with the atomic symbol Se, atomic number 34, and atomic weight 78.97. It is an essential micronutrient for mammals and other animals but is toxic in large amounts. Selenium protects intracellular structures against oxidative damage. It is an essential component of. Chemical elements listed by atomic number The elements of the periodic table sorted by atomic number. Click on any elements name for further chemical properties, environmental data or health effects. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. Name: Selenium Symbol: Se Atomic Number: 34 Atomic Mass: 78.96 amu Melting Point: 217.0 °C (490.15 K, 422.6 °F) Boiling Point: 684.9 °C (958.05005 K, 1264.8201 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 34 Number of Neutrons: 45 Classification: Non-metal Crystal Structure: Hexagonal Density @ 293 K: 4.79 g/cm 3 Color: gray Atomic Structure. Answer the following questions about the element selenium, Se (atomic number 34). (a) Samples of natural selenium contain six stable isotopes. In terms of atomic structure, explain what these isotopes have in common, and how they differ. The isotopes have the same number (34) of protons, but a different number of neutrons. Selenium atoms have 34 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.6. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral selenium is Ar.3d 10.4s 2.4p 4.
Se Atomic Mass
The atomic mass is useful in chemistry when it is paired with the mole concept: the atomic mass of an element, measured in amu, is the same as the mass in grams of one mole of an element. Thus, since the atomic mass of iron is 55.847 amu, one mole of iron atoms would weigh 55.847 grams. The same concept can be extended to ionic compounds and molecules. One formula unit of sodium chloride (NaCl) would weigh 58.44 amu (22.98977 amu for Na + 35.453 amu for Cl), so a mole of sodium chloride would weigh 58.44 grams. One molecule of water (H2O) would weigh 18.02 amu (2×1.00797 amu for H + 15.9994 amu for O), and a mole of water molecules would weigh 18.02 grams.
Se Atomic Number Definition
The original periodic table of the elements published by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869 arranged the elements that were known at the time in order of increasing atomic weight, since this was prior to the discovery of the nucleus and the interior structure of the atom. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number instead.
Chemical properties of selenium - Health effects of selenium - Environmental effects of selenium
|


|
Humans may be exposed to selenium in several different ways. Selenium exposure takes place either through food or water, or when we come in contact with soil or air that contains high concentrations of selenium. This is not very surprising, because selenium occurs naturally in the environment extensively and it is very widespread. Overexposure of selenium fumes may produce accumulation of fluid in the lungs, garlic breath, bronchitis, pneumonitis, bronchial asthma, nausea, chills, fever, headache, sore throat, shortness of breath, conjunctivitis, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and enlarged liver. Selenium is an eye and upper respiratory irritant and a sensitizer. Overexposure may result in red staining of the nails, teeth and hair. Selenium dioxide reacts with moisture to form selenious acid, which is corrosive to the skin and eyes. Carcinogenicity- The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has listed selenium within Group 3 (The agent is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans.) |
Effects of selenium on the environment
Low levels of selenium can end up in soils or water through weathering of rocks. It will than be taken up by plants or end up in air when it is adsorbed on fine dust particles. Selenium is most likely to enter the air through coal and oil combustion, as selenium dioxide. This substance will be converted into selenium acid in water or sweat. |
Sources of periodic table.
Back to the periodic table of elements.
Se Element Charge
More from 'Elements'
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Se Atomic Number Meaning
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Se Atomic Number Symbol
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Se Atomic Number Periodic Table
Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved

